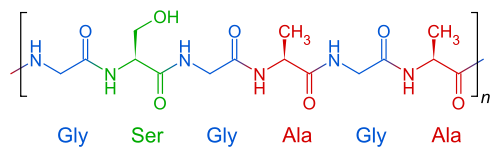
Primary structure of proteins
The primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in the protein, ordered from the first amino acid to the last. Therefore, it indicates the amino acids that make up the polypeptide chain and in what order they are found. The function of each protein depends on its sequence of amino acids that make it up and the form it takes.
All proteins have two ends:
- An N-terminal end in which the first amino acid with its free amino group is found, which is why it is called the N-terminal amino acid.
- A C-terminal end, in which the last amino acid with its free carboxyl group is located, which is why it is called the C-terminal amino acid.