Dialysis
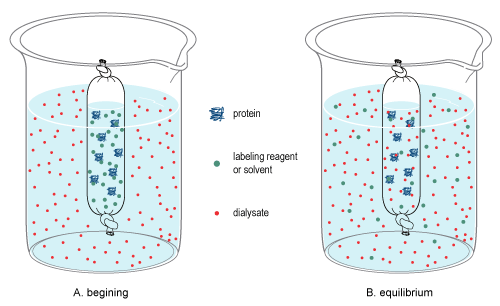
The dialysis is the process of separating the colloidal particles, depending on their size, through a dialyser membrane. This membrane allows the passage of small molecules (mineral salts, ions) and water and prevents the passage of macromolecules or colloidal particles.
When the membrane that separates two solutions allows the smaller solutes to pass, in addition to water, the phenomenon called dialysis occurs. Low molecular weight molecules pass from the solution in which they are in the highest concentration to the solution in which they are in the lowest concentration.
Potcherboy de Wikipedia en inglés [CC BY 3.0], undefined
The hemodialysis is the treatment used to clean the blood in cases of chronic renal failure by using a filter or hemodialyzer and dialysate generated by an artificial kidney. Small molecules from the blood pass into the dialysis fluid through the membranes used. Thus, water, urea, mineral salts, ... which cannot be filtered by the kidney in a natural way, are eliminated .
 By Freemesm (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
By Freemesm (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons