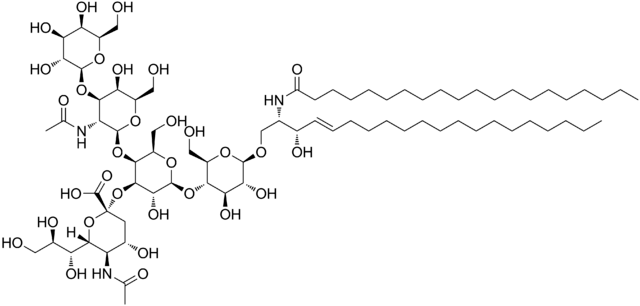
Glycolipids (or sphingoglycolipids)
They are complex lipids formed by the union of:
- A ceramide (sphingosine attached to a fatty acid).
- A carbohydrate.
They lack a phosphate group and do not have ester bonds either.
They are part of the lipid bilayers of the cytoplasmic membranes of all cells, especially neurons in the brain.
Glycolipids are part of the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The carbohydrate part of the molecule is oriented towards the outside of the plasma membrane and is a fundamental component of the glycocalyx, where it acts in cell recognition and as antigenic receptors.
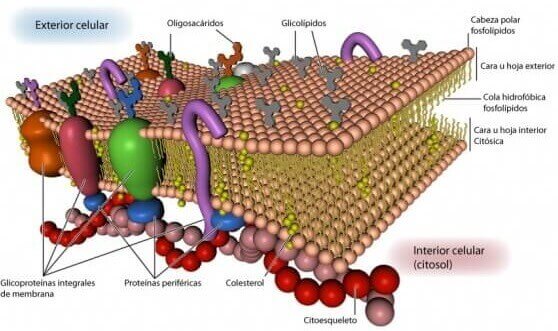
The glycolipids can be divided into two groups: