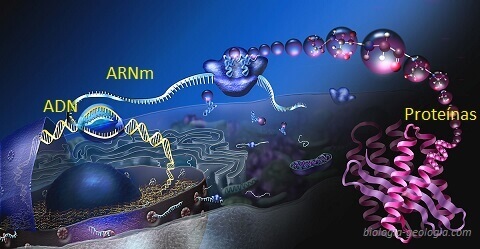
DNA to RNA transcription. RNA synthesis.
After Beadle and Tatum, in 1948, established the parallelism between genes and enzymes (one gene-one enzyme theory), and Watson and Crick, in 1953, proposed the double helix model of DNA, Crick proposed his hypothesis of collinearity. This hypothesis says that there is a correspondence between the nucleotide sequence of a gene and the amino acid sequence of the enzymes that the gene encodes.
Two processes are distinguished within the mechanism of the passage from nucleotide sequence to amino acid sequence.
- Transcription: It takes place in the nucleus, where a sequence of deoxyribonucleotides of a gene (DNA) is passed to a sequence of ribonucleotides with complementary nitrogenous bases of mRNA.
- Translation: In ribosomes, you go from a sequence of ribonucleotides of mRNA to a sequence of amino acids.
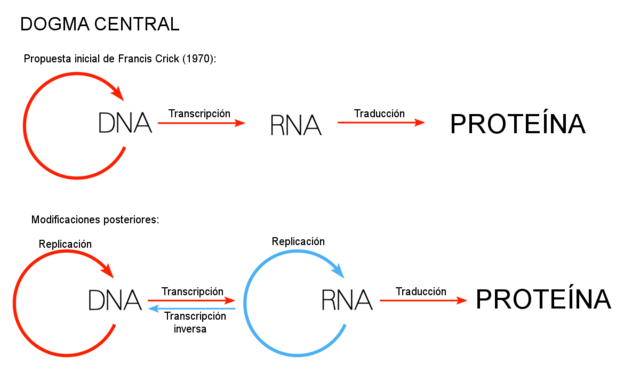
These processes constitute the basis of the central dogma of molecular biology, although it has had to be modified by current knowledge of the replication of some viruses: