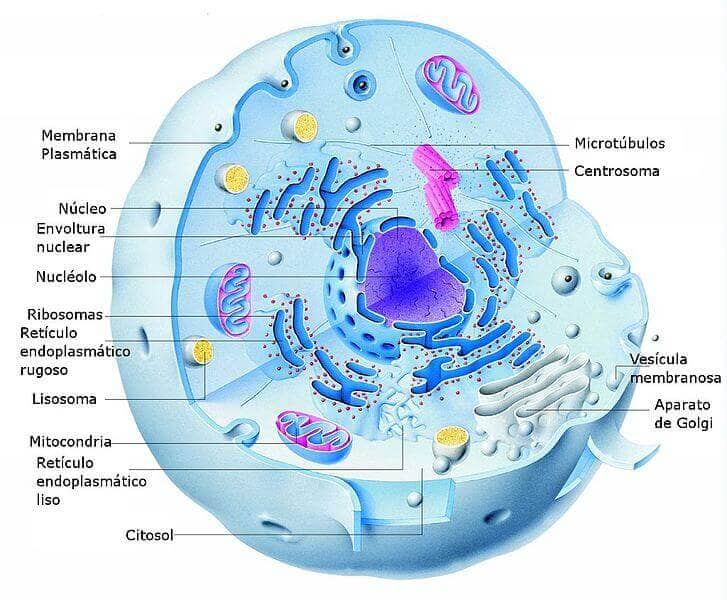
Eukaryotic cell
The eukaryotic cell is characterized by having the genetic material (DNA) surrounded by a nuclear membrane. There are unicellular organisms made up of a single eukaryotic cell and others, such as plants, animals, fungi, algae, etc., that are multicellular and are made up of many eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells have the following structure:
- The plasma membrane. The cell is surrounded by a thin shell that regulates the entry and exit of substances, protects the cell, and where structures that allow cell movement can be found, such as cilia and flagella.
- The cytoplasm. It is the internal space of the cell in which are all the substances necessary for the life of the cell. In the cytoplasm are the different cellular organelles that perform different functions.
- The Core. Membrane that surrounds the genetic material, whose DNA is organized in structures called chromosomes.
Eukaryotic cells have organelles that assist in cell function. For example:
- Mitochondria, responsible for obtaining energy.
- Ribosomes, which synthesize proteins.
- Chloroplasts, which carry out photosynthesis in plant cells.
- Lysosomes, which break down substances transforming them into simpler ones usable by cells.
There are two types of eukaryotic cells:
- Plant eukaryotic cells.
- Animal eukaryotic cells.