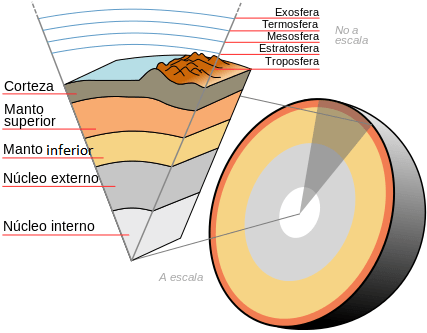
Characteristics of the geosphere
The Earth and the rest of the Solar System were formed about 5000 million years ago from a nebula, a large cloud of gas made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, and of cosmic dust. The explosion of a supernova could originate an expansive wave that caused the movement of the particles and the formation of a large disk.
The materials were concentrated by the action of gravity, originating a great mass of hydrogen and helium whose temperature increased until thermonuclear fusion reactions took place and originated the Sun.
The rest of the matter revolved around the Sun and they were grouped into planetesimals that collided and fused to give rise to the planets, which were balls of incandescent materials. These molten materials were grouped in layers according to their density. The densest materials sank to the interior of the Earth, and the less dense remained in the outer layers and around the Earth.
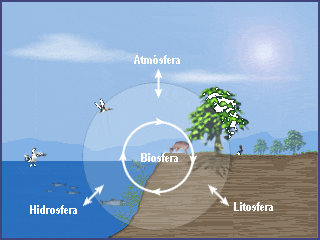
In this way, the structure of the Earth is made up of a series of concentric layers. The solid part, the geosphere, is divided into several layers, surrounded by another gaseous layer, the atmosphere. As it cooled, the water vapor condensed and formed liquid water, which accumulated until forming the hydrosphere. In addition, life arose throughout the Earth, occupying its surface, and constituted the biosphere.
Therefore, it can be said that the Earth is divided into four layers:
- Geosphere: it constitutes the solid part of our planet, characterized by the relief of its surface and by the layers that compose it. In this topic we are going to focus on how the geosphere is constituted.
- Atmosphere: it is the layer formed by the gases that form the air and that surrounds the Earth. Its existence is vital for living beings.
- Hydrosphere: it is formed by all the existing water on Earth.
- Biosphere: Although it is not really a layer, it includes all the ecosystems on Earth. That is, living beings and the environment in which they inhabit.
 By Bojana Petrović [CC BY-SA 4.0 ], from Wikimedia Commons
By Bojana Petrović [CC BY-SA 4.0 ], from Wikimedia Commons
Interactive activity: The layers of the Earth.
Interactive activity: The layers of the Earth (2).
Interactive activity: Order these materials.