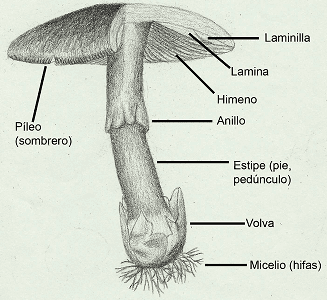
Fungi kingdom
The fungi kingdom or fungi kingdom is made up of eukaryotic organisms that can be unicellular, such as yeasts, or multicellular, such as molds and mushrooms. They are characterized by having a cell wall of chitin (not of cellulose like plants), and their cells are not differentiated into true tissues, but instead group together to form filaments called hyphae, the whole of which is called mycelium.
Although they feed by absorption, like plants, they are heterotrophs. They do not have chlorophyll nor do they photosynthesize.
Vital functions of fungi
Function of nutrition in fungi
Fungi are heterotrophs. That is, they need organic matter already made by other organisms. Depending on how they get their food, these types of fungi are distinguished:
- Saprophytes or decomposers. They are fungi that live on the remains of dead animals or plants or on their excrement. Its performance is essential in the formation of humus. They are responsible for recycling dead organic matter, transforming it into inorganic matter that can be used again by plants.
Video: Parasitic fungus of an ant.
- Parasites. They get their food, organic matter, from other living beings that cause diseases called mycoses, such as ringworm and athlete's foot.
- Symbiotics. These are fungi that live in association with other living beings (plantsoranimals) for mutual benefit. For example,lichens,formed by the association of an algae and a fungus. Thefungusis responsible for absorbing and retaining water and mineral salts that it gives to the algae. Thealga,in turn, performs photosynthesis and provides organic matter to the fungus.
Lichens are very important in the colonization of rocks, which they slowly transform into soil on which vegetation and the rest of the ecosystem can later develop. They are sensitive to contamination and are therefore used as biological indicators of contamination.
Interactive activity: Lichens.
Interactive activity: Lichens.
Enlargement: Main species of lichens.
Relationship function in fungi
Fungi live fixed to the substrate on which they develop (soil, fruits, plants, etc.). Although they do not have structures for locomotion, such as cilia or flagella, and cannot move, their filaments can grow rapidly to respond to needs in the environment, such as for food.
Reproductive function in fungi
Fungi reproduce by spores. A reproductive structure stands out, the mushrooms.