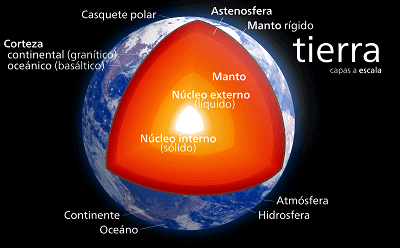
Structure and composition of the Earth's core
The core is the innermost part of the Earth, made up of iron and a little nickel, sulfur, and oxygen. Two parts are distinguished:
- Outer core: fluid, from 2,900 km to 5,100 km.
- Inner core: solid, from 5100 km to 6370 km.
Temperatures are very high, and this internal heat is responsible for the internal geological processes that generate earthquakes, volcanoes or the displacement of tectonic plates.
The convection currents that occur in the outer core are the cause of the Earth's magnetic field.