Sexual reproduction in plants
Sexual reproduction in plants consists of several stages:
Sexual reproduction in plants consists of several stages:
The flower of an angiosperm is a modified short stem, with leaves modified to perform the functions of gamete production. The flower is attached to the stem by a peduncle, and is made up of highly specialized leaves, which form different groups orwhorls. If they distinguish four types of whorls :
According to this, a flower can be:
Flowers often appear next to each other forming structures called inflorescences , such as clusters, the ears and umbels.
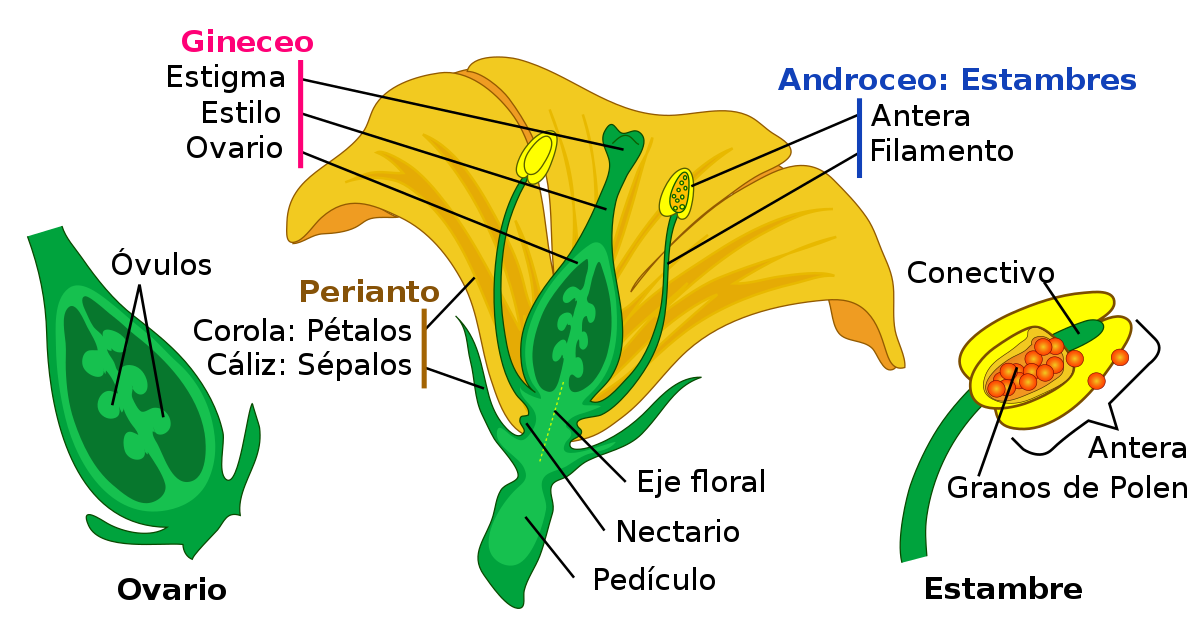 De Mariana Ruiz LadyofHats, translation by Serg!o - traducción de Image:Mature flower diagram.svg, Dominio público, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3732982
De Mariana Ruiz LadyofHats, translation by Serg!o - traducción de Image:Mature flower diagram.svg, Dominio público, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3732982
Interactive activity: Point out which image is a gymnosperm whose flower is a pineapple.
Game: Flower parts puzzle.
Pollination is the process of pollen transfer from the time it leaves the stamens until it reaches the stigma of flowers in angiosperms. There, in the pistil, the ovules that will give rise to the seeds and fruits are fertilized.
Pollination can be:
When the pollen grain reaches the stigma (female part) of the flower, a pollen tube is formed that grows through the style until it reaches the ovary.
The male gamete travels down the pollen tube to the ovary, where it joins the female gamete and the zygote is produced.
Fertilization is the union of the male and female gamete.
Angiosperms are plants that are characterized by producing seeds that are contained within a fruit.
The zygotes (fertilized ovules) transform into seeds, in which three parts are distinguished:
The ovary of the flower also develops and forms the fruit, which will protect the seeds and facilitate their dissemination. When the fruits ripen, the seeds are released and disperse.
The dispersion of the fruit or the seed can be carried out by the action of the wind, other animals, etc., and allows the plant to colonize other places. For this reason, the fruits usually have characteristics that facilitate their dispersion.
When it falls to the ground, if the conditions are right (time of year, temperature, humidity, etc.), the seed will begin to germinate. The seed absorbs water and swells until the protective cover is broken. The embryo begins to grow, appearing a small root that penetrates the soil, and one or two leaves (cotyledons) that will continue to develop until forming a new plant.
The seeds can wait for germination for many years, until they find the right conditions for their development.
Interactive activity: Phases of plant reproduction.
Obra publicada con Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento Compartir igual 4.0