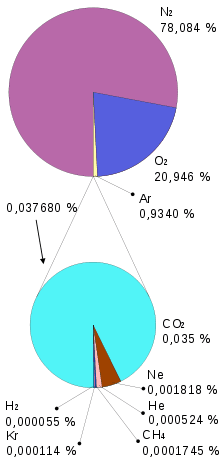
- Smog (from smoke, smoke, and fog, fog). Mists of polluting substances produced when pollution is combined with a long period of anticyclonic situation (high pressures) that causes stagnation of the air and that pollutants are not dispersed.
Regional effects of air pollution
The main regional or transboundary effect is acid rain, produced by reacting rainwater with oxides of sulfur and nitrogen from the burning of fossil fuels, causing sulfuric and nitric acid that cause damage to the soil, water, in the vegetation, and that can even affect limestone rocks of old constructions, causing the well-known stone malady.
Global Effects of Air Pollution
Among the main global effects, we must highlight those produced in the ozone layer. The ozone (O3) layer is an area of the stratosphere that acts as a protective shield against ultraviolet radiation that comes from the Sun. The use of CFCs contained in sprays and refrigerants, along with other pollutants, has caused the layer to decrease. its thickness (hole in the ozone layer) putting our health at risk.
The natural greenhouse effect is good and, thanks to it, life can exist on Earth. Part of the radiation that comes from the Sun is reflected by the Earth, while other part reaches the surface and heats the Earth. As the Earth warms, it emits infrared radiation that, instead of escaping, part of it is retained (by water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxides, etc.) and reflected back to Earth. This is the greenhouse effect .
With air pollution there has been an increase in the greenhouse effect in an artificial way that contributes to climate change.