Other current theories about evolution
Some other theories about evolution are:
- Theory of punctuated equilibrium or punctuality or intermittent equilibrium.
- Neutralist theory or neutralism.
- Selfish gene theory.
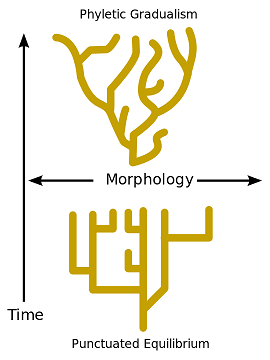
Theory of punctuated equilibrium or punctualism or intermittent equilibrium
When studying the fossil record, paleontologists questioned the gradualism asserted by the synthetic theory of evolution. If gradualism were true, there should be a multitude of fossils with intermediate characteristics between one species and another, showing a slow and continuous change in evolution. But in many cases, one species suddenly disappears and another appears.
According to some paleontologists, such as Stephen Jay Gould, they believe that the theory of punctuated or intermittent equilibrium (1972) is more correct. According to this theory, species spend a long time without any change or with minor changes (periods of time called stasis), but at certain times, some species have periods of very rapid change.
Punctualism should not be confused with saltationism. The saltationism postulates that appear new species in a single generation, and punctualism is not in favor of that.
The punctualism does not deny the neo - Darwinism, but proposes an explanation for cases in which a rapid diversification of species occurs.
For example, in the Cambrian there was a great diversification of species that could not be explained by the gradualism of Neo - Darwinism.
By Miguel Chavez, modified by wooptoo (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons