The cell cycle
Cell, prokaryotic or eukaryotic, reproduce to give rise to new daughter cells which, after growing and fulfilling their functions, will reproduce again to give rise to new cells.
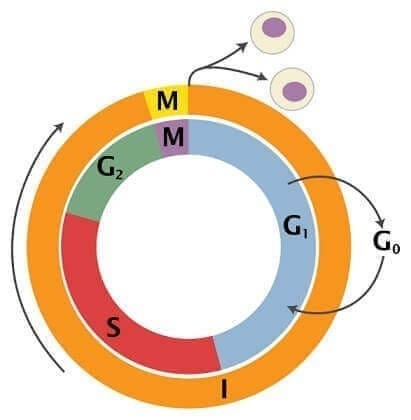
The cell cycle is the sequence of events that take place from the time a cell originates by division of a previous cell, until it divides again to give rise to new daughter cells.
Although almost all cells can divide, there are some exceptions. Muscle cells or neurons cannot divide. Others, such as those of the intestinal epithelium, usually take about 8 hours to divide.
For many single-celled organisms, the cell cycle constitutes their life cycle and the birth of a new organism.
For multicellular organisms, the cell cycle of their cells allows their growth and the repair of damaged tissues.
In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two stages: