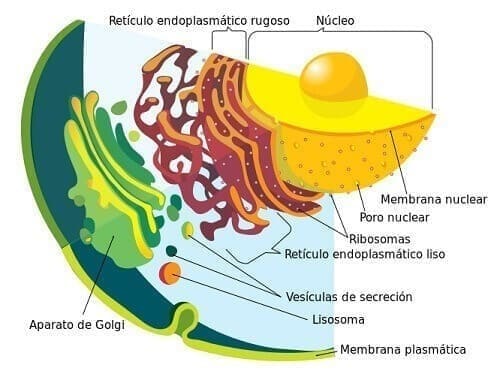
Plasma membrane
The plasma membrane delimits the cell, regulates the passage of substances and receives stimuli from the external environment. It is made up of a double layer of lipids with proteins and carbohydrates.
- The lipids prevent the passage of polar substances.
- The proteins are among the lipids, creating channels through which can pass some substances.
- The carbohydrates are only on the outside of the membrane and are responsible for receiving information from the outside of the cell.

By This SVG image was created by Medium69.Cette image SVG a été créée par Medium69.Please credit this : William Crochot (NIST) [Attribution or CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the space between the plasma membrane and the cell nucleus. It is composed of:
Ribosomes
The ribosomes are small membranous organelles not may be isolated, dispersed in cytosol, or attached to the membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. They are made up of RNA and proteins.
They are responsible for synthesizing proteins from the information provided by the messenger RNA from the nucleus (where the DNA is).
Cilia and flagella
The cilia and flagella are extensions of the membrane formed by microtubule protein.
- The cilia are short and numerous, and may cover all or part of the surface of the cell.
- The flagella are long and few in number.
Its function is to allow cell movement or to produce small currents in the external environment to capture nearby nutrients.

By Kohidai, L. (File:Flagellum-beating.svg) [CC BY 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons