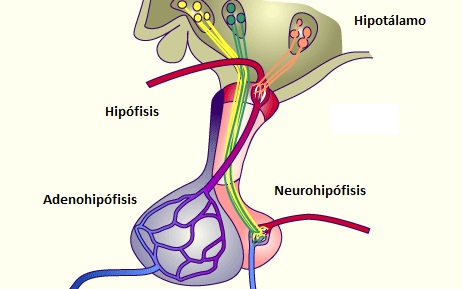
Thyroid and parathyroid
The thyroid and parathyroid glands are endocrine glands located in the front part of the neck, surrounding the trachea and larynx.
The thyroid is an endocrine gland regulated by the pituitary gland and secretes two types of hormones:
- The thyroxine, the most important hormone produced by the thyroid, contains iodine. Its effects on the body are:
- It is responsible for regulating the body's metabolism and the body's sensitivity to other hormones.
- When the body is growing, growth hormone (GH) stimulates the increase in size, while thyroxine causes the tissues to take the appropriate shape as they grow. That is, thyroxine makes tissues develop in the proper shapes and proportions.
- The calcitonin, which promotes ossification because it reduces the level of calcium in the blood by stimulating their deposition in bones.
When an excess of thyroid secretion occurs, a disease called hyperthyroidism appears. The deficit produces hypothyroidism. Both diseases will be discussed later.
The parathyroid glands are located behind the thyroid. It secretes the parathormone that produces the increase of calcium in the blood, releasing it from the bones. Its function is antagonistic to calcitonin.

By unknown for original image[1]Miguelferig for the Galician annotation (File:Illu thyroid parathyroid.jpg) [CC0 or Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
Activity: Thyroid and parathyroid.