The digestion
The digestion is the transformation of foods, previously ingested into simpler substances that can be absorbed and utilized by the cells![]()
![]() .
.
Throughout the digestive tract, food is transformed into different substances. Digestion can be of two types:
- Mechanical digestion. The food is fragmented, kneaded, mixed, etc.
- Chemical digestion. Some substances, such as digestive enzymes, are responsible for breaking down food, aided by other chemicals. These substances are secreted by the walls of the digestive tract and by the adjacent glands.
Digestion begins in the mouth, when the amylase or ptyalin enzyme contained in saliva begins to chemically digest carbohydrates. In addition, the teeth and the tongue facilitate this digestion with their mechanical action.
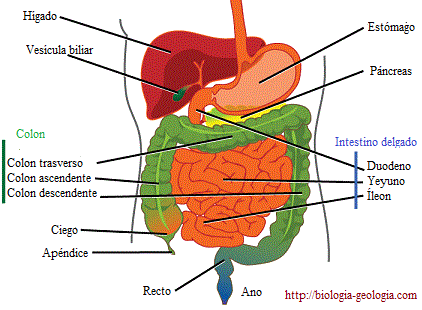
But the most important digestion processes occur in the stomach and small intestine, where the pancreas and liver also play a role in digestion.