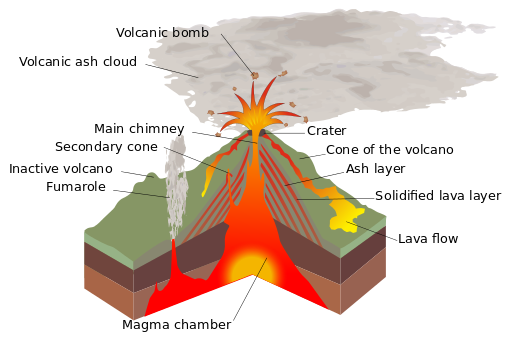
Volcanoes
A volcano is a geological structure through which incandescent materials, magma (lava and gases) come out from the interior of the Earth. The internal energy of the Earth causes the temperature and pressure to increase with depth, reaching a temperature of about 5000 ºC in the Earth´s core.
When these materials subjected to high pressure and temperature meet an area where the pressure is lower (some fracture), they melt, the magma rises to the surface and the volcano erupts. When the lava goes outside, it cools and solidifies, increasing each time the volcanic cone.
Volcanoes, generally, are found on the limits of tectonic plates (for example, in the ridges), which is where the magma has more facility to go to the outside. There are also volcanoes that appear inside the tectonic plates in the spots hot or hot spots, with rising materials from the lower mantle, like the Hawaiian Islands, which leaves the lava at about 1200 °C.
Volcanic eruptions vary greatly in intensity, duration, and frequency, and can be gentle lava flows or explosive eruptions. Volcanoes can be located above sea level or be underwater.