Parts of the female reproductive system
The parts of the female reproductive system are:
By KES47 (File:Scheme female reproductive system-en.svg) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons

By Bibi Saint-Pol [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
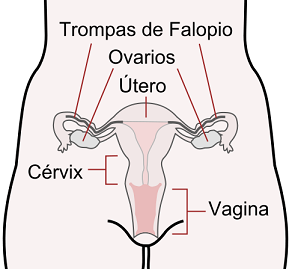
- The ovaries. They are the female gonads, about the size of an almond, and are housed in the abdomen. Inside are circular structures, the ovarian follicles, which contain the ovules (female gametes). The eggs are released one by one every 28 days or so.

The ovaries also secrete the female sex hormones responsible for the secondary sexual characteristics of women and the regulation of the ovarian cycle.
- The fallopian tubes or oviducts. They are two tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. They are responsible for carrying the egg to the uterus. This is where fertilization occurs, that is, the union of an egg with a sperm
 .
.
- The uterus or womb. It is the muscular cavity into which the fallopian tubes flow, it houses the zygote or fertilized ovum and is the place where the embryo develops during pregnancy.
The internal part of the uterus is covered by a mucosa, the endometrium, formed by highly vascularized tissue whose function is to nourish the embryo. If fertilization does not occur, the endometrium is expelled, leading to menstruation.
In the lower part, the cervix or cervix, the uterus narrows and communicates with the vagina.
- The vagina. It is the elastic duct, with muscular walls lined by a mucosa, which communicates the uterus with the outside, welcomes the male penis and where the semen is deposited. It is the copulatory organ and the conduit through which the fetus exits during childbirth.
It has glands that secrete lubricating substances to facilitate the introduction of the penis. At the entrance to the vagina there is a small incomplete membrane called the hymen that usually breaks during the first sexual intercourse.
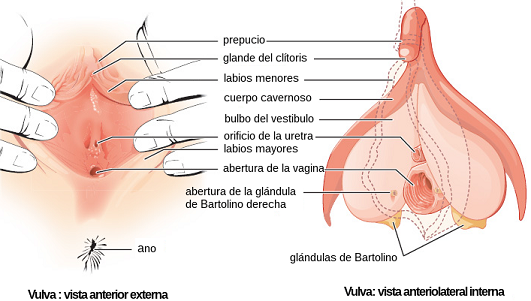
- The vulva. It is the external genital organ, formed by two folds of skin called the labia majora and minora that cover the vaginal opening and the urinary meatus
 .
.
At the top, where the labia minora meet, is the clitoris, a small, very sensitive erectile organ with many nerve endings.
The Bartholin's glands, located on both sides of the vaginal opening, produce fluids that lubricate the vagina to facilitate copulation.
- The mammary glands. They are responsible for producing milk that will serve as food when the baby is born .
By OpenStax College;CFCF, Turdas, and myself (Figure_28_02_02.jpg) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons



