The bones
Bones are living organs made up of collagen and calcium and phosphorus salts, which give it hardness.
Several parts of the bone are distinguished:
- Epiphysis: are the ends of the long bones. They are very light because they are made up of spongy bone tissue. It is the area that engages in the joints.
In the spaces left by the spongy bone tissue is the red bone marrow, responsible for the production of blood cells.
- Diaphysis or cane: it is the elongated part of the bone that is between the epiphyses. It is made up of compact bone tissue, which provides rigidity to the bone. It contains quite a few nerves and capillaries.
In the central part of the diaphysis is the medullary cavity, which contains adipose tissue that constitutes the yellow bone marrow![]() .
.
- Metaphysis: is the area of union between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. In times of growth it contains cartilage, which will later be replaced by bone tissue.
- Processes: they are the projections of the bone, where the muscles, ligaments and tendons are inserted.
- Periosteum: it is a membrane that covers the bone, although it is not present in the joints (epiphysis), since it is replaced by cartilage, which protects from friction.
- Endostium: membrane of connective tissue that lines the medullary cavity.
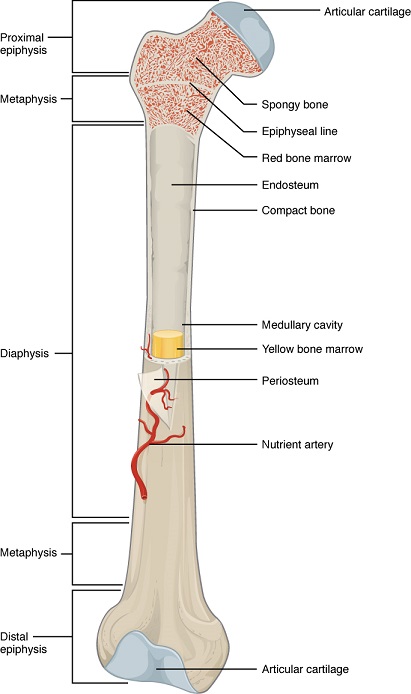
By OpenStax Anatomy and PhysiologyOpenStax [CC BY 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons